Specialist treatment for all types of arthritis
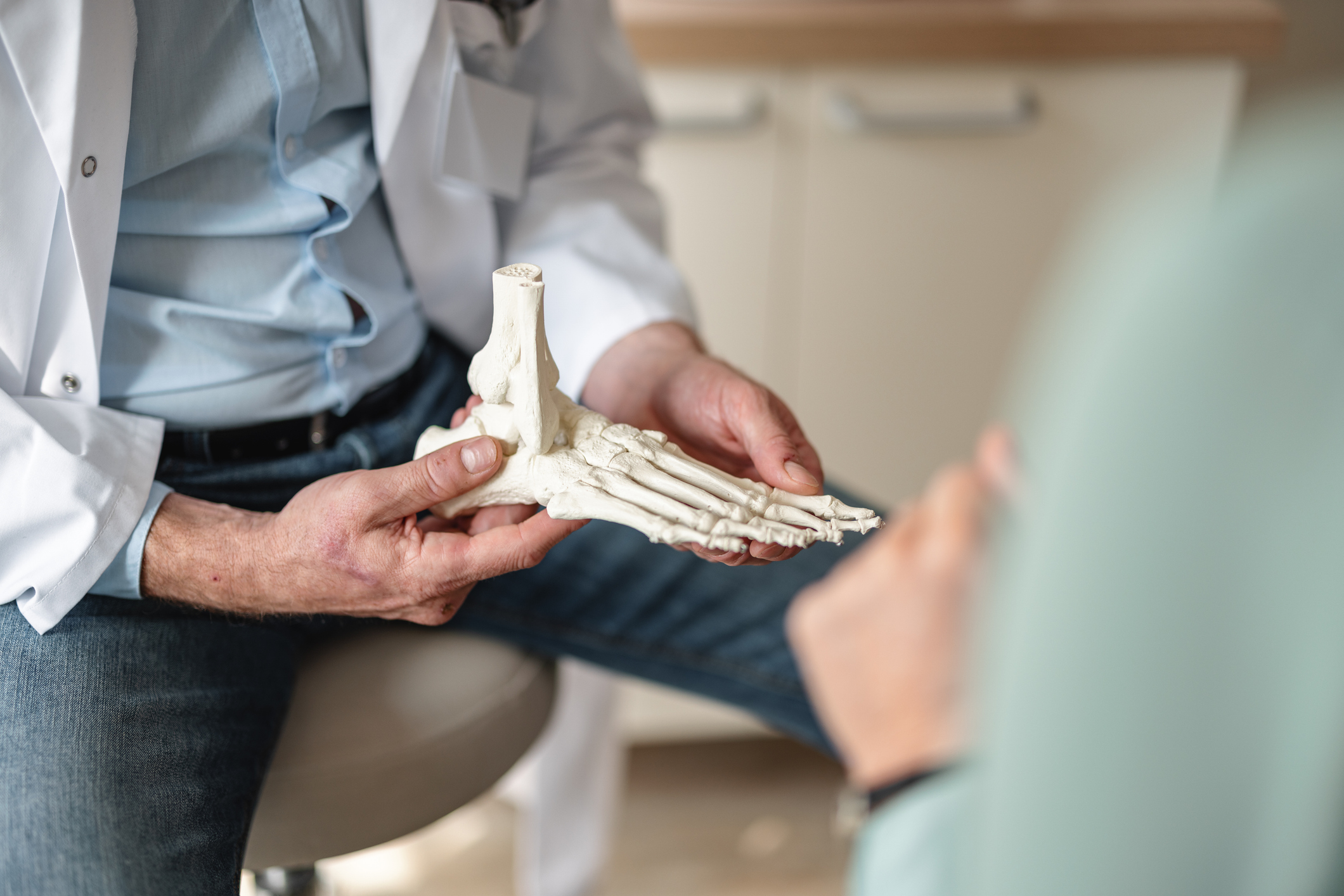
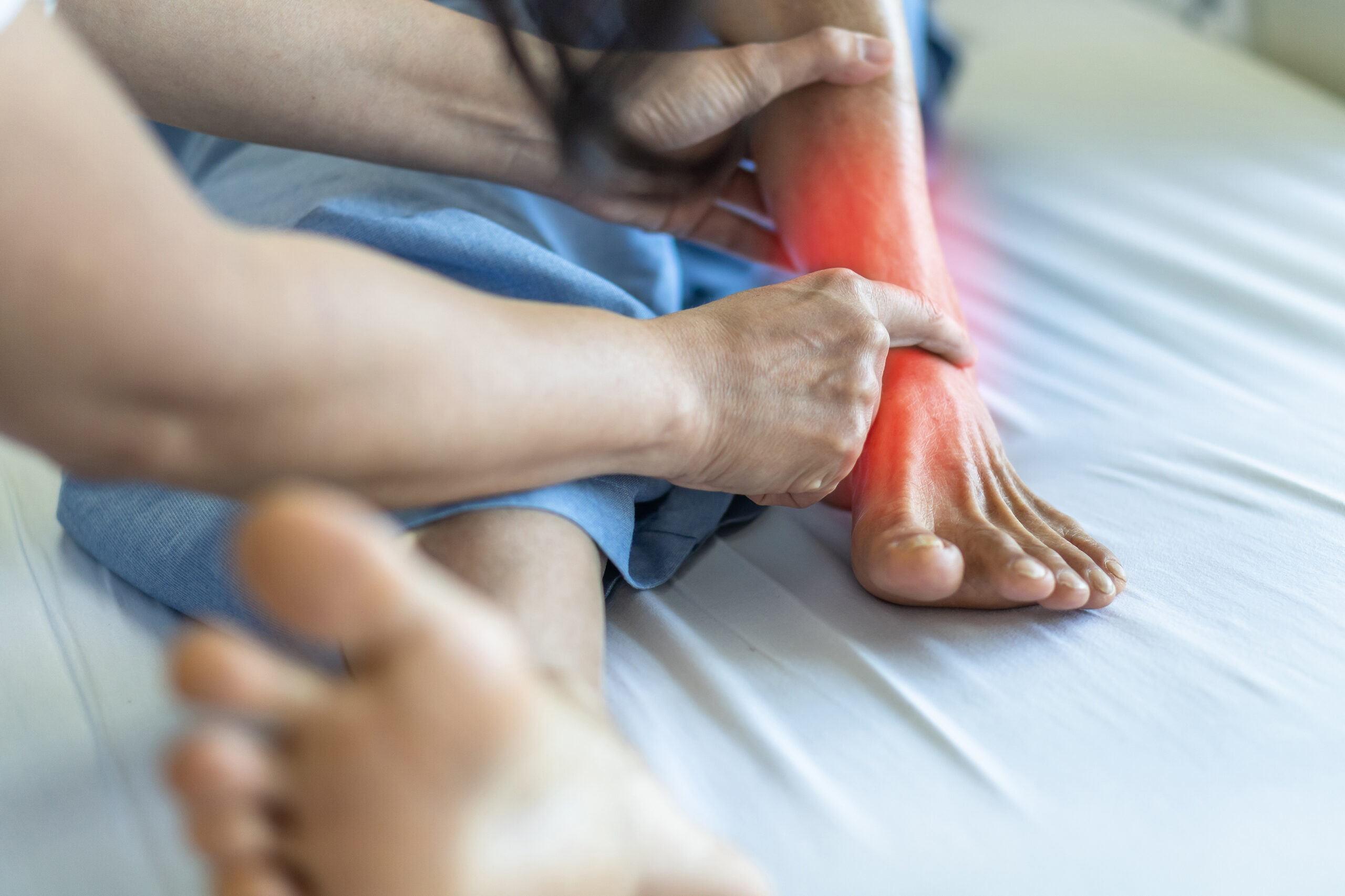
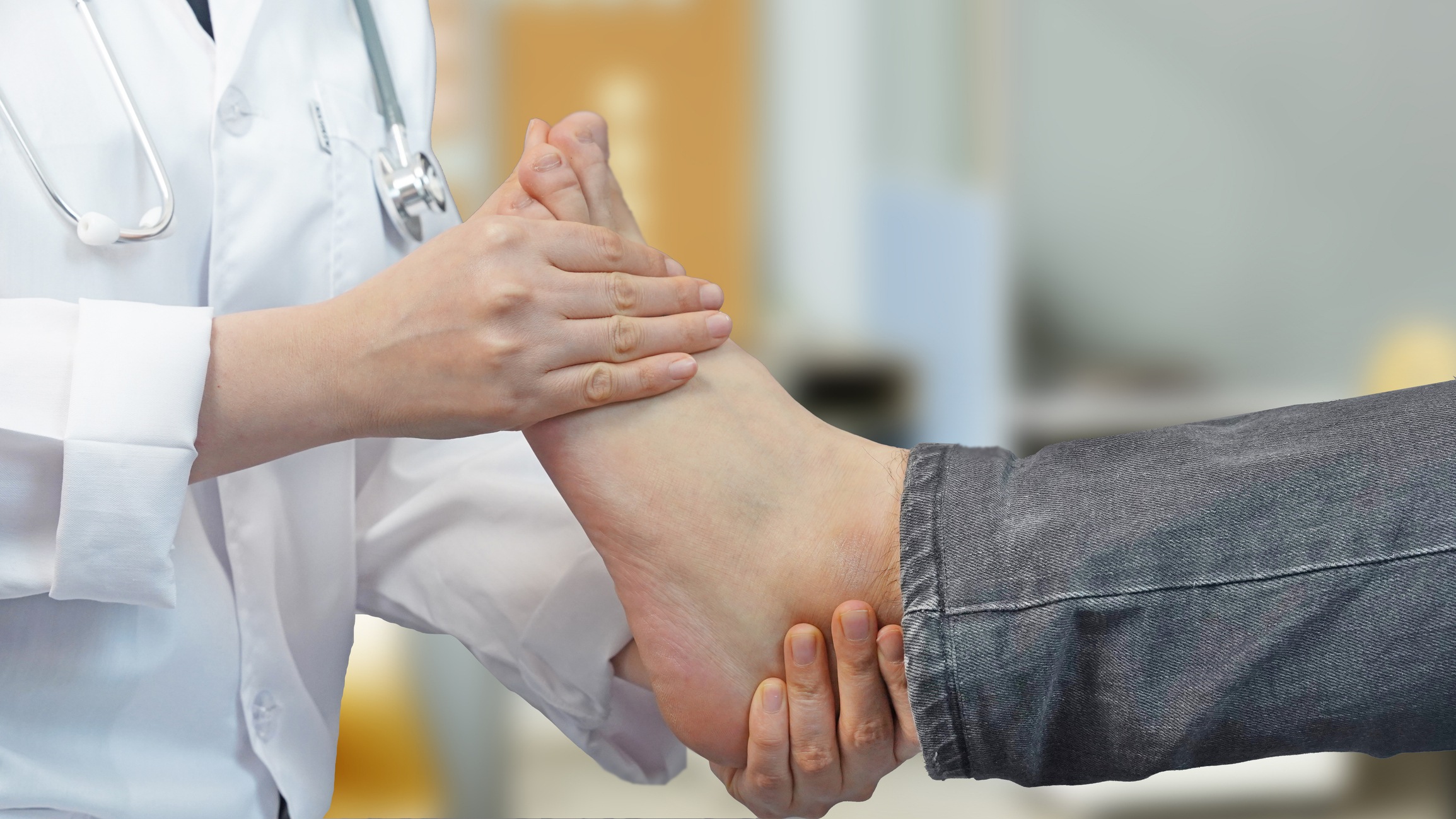
Arthritis can affect mobility and wellbeing for people of all ages. It is a common and diverse group of conditions involving inflammation of the joints and causing pain, stiffness and swelling. With over 100 different types, arthritis affects people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds, making it one of the leading causes of disability globally.
Book your appointment